Is diabetes remission possible?
Yes
How is diabetes remission defined?
Diabetes remission is defined as HbA1c (the average of last 3 months blood glucose) below 6.5% without any diabetes medicines for at least 3 months
Is there a difference between diabetes remission and reversal?
Diabetes reversal implies that diabetes has been totally cured and no further adjustments are required in lifestyle. That is unlikely to happen.
Even though diabetes medicines can be stopped with proper measures, but lifestyle changes are necessary to maintain remission. Reverting to an erratic lifestyle can elevate blood glucose levels and medicines may have to be restarted.
So, diabetes remission is the preferred term rather than reversal or cure.
What is the science behind diabetes remission?
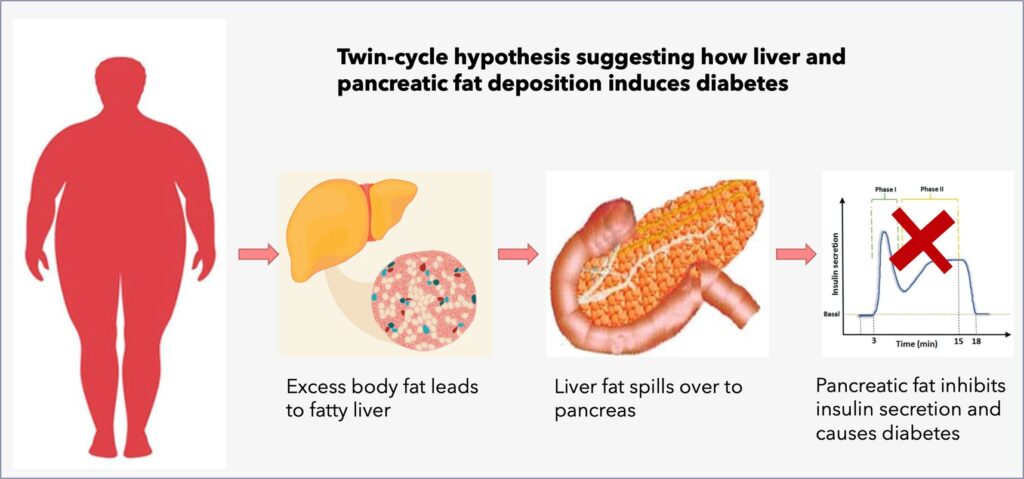
The guiding principle behind diabetes remission is weight loss and reduction of fat content from the body in general and subsequently from liver and pancreas.
Scientists have demonstrated that when fat stores in liver are full, fat spills out and deposits in other organs including pancreas. Excess fat in the pancreas diminishes insulin secretion. When excess fat is present in the pancreas for a long duration, there is permanent damage to the insulin secretory cells of the pancreas and diabetes becomes irreversible.
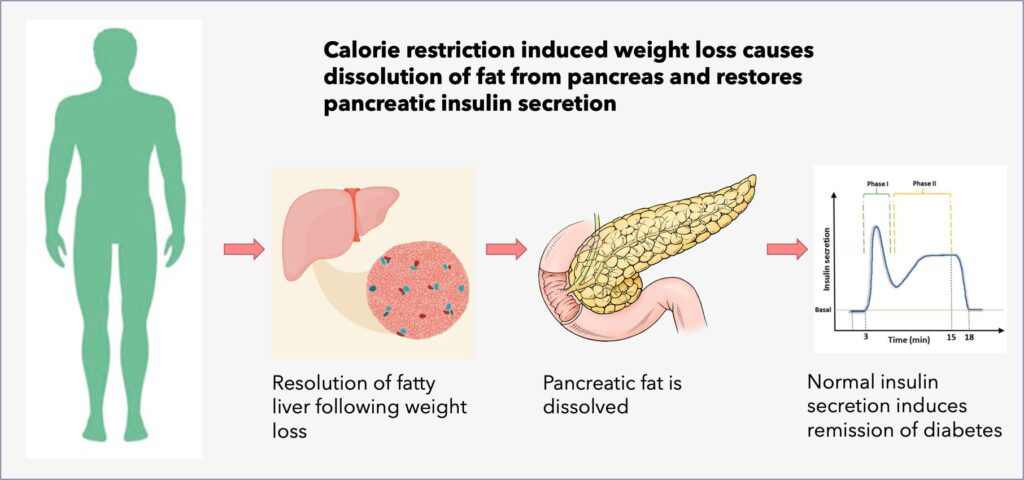
A very low-calorie diet for around 2 months duration causing weight loss also leads to dissolution of fat from liver and pancreas. Removal of pancreatic fat restores the insulin secretory mechanism and induces diabetes remission.
Long-standing diabetes where the pancreatic fat deposition has resulted in permanent damage might not remit.
Do you fit into the criteria for undergoing trial of diabetes remission
- Type 2 diabetes
- Onset of diabetes < 6 years
- Obesity (BMI > 25)
- Not on insulin
- No major comorbidities
- Age> 18 years
- Not pregnant or lactating
Services we offer to achieve diabetes remission
- Screening and checking your eligibility
- Prescribing a very low-calorie diet plan
- Guiding you during the 2 months of low-calorie diet
- Monitoring essential parameters and assessing safety
- Suggesting a follow-up diet plan
- Intervene when necessary
Further reading
- Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, Brosnahan N, Thom G, McCombie L, etal. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet. 2018 Feb 10;391(10120):541-551. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33102-1. Epub 2017 Dec 5. PMID: 29221645.
- Taylor R. Type 2 diabetes and remission: practical management guided by pathophysiology. J Intern Med. 2021 Jun;289(6):754-770. doi: 10.1111/joim.13214. Epub 2020 Dec 27. PMID: 33289165; PMCID: PMC8247294.
- Taylor R. Banting Memorial lecture 2012: reversing the twin cycles of type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013 Mar;30(3):267-75. doi: 10.1111/dme.12039. PMID: 23075228; PMCID: PMC3593165.
